Virtualisation is a core part of modern computing, yet it often operates behind the scenes, invisible to end users and even some IT decision-makers. For many businesses, it has become a fundamental part of how IT systems are deployed, managed, and scaled. But how did we get here, and what exactly is virtualisation?
In this post, we’ll explore the origins of virtualisation, its impact on IT infrastructure, and why it’s still relevant — particularly for small businesses and growing enterprises looking to make efficient use of hardware resources.
What Is Virtualisation?
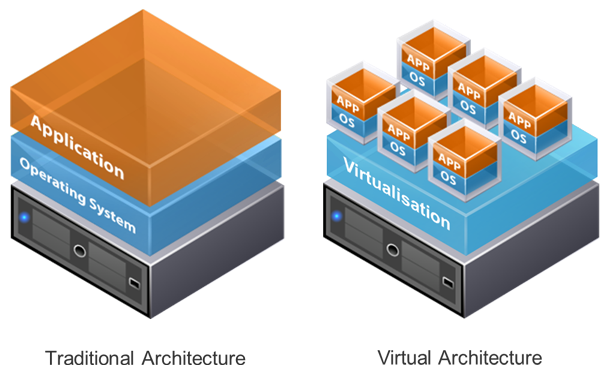
Virtualisation is the process of creating a virtual (rather than physical) version of something — typically a server, desktop, storage device, or network resource.
The most common example is server virtualisation, where one physical server runs multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM operates as a separate system with its own operating system, resources, and software stack. All of this is managed by a hypervisor, a layer of software that separates the virtual machines from the underlying hardware.
There are two main types of hypervisors:
- Type 1 (bare-metal) – runs directly on the host hardware (e.g., VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, Proxmox VE).
- Type 2 – runs on top of a host OS (e.g., VirtualBox, VMware Workstation).
A Brief History of Virtualisation
Virtualisation isn’t a new concept. It dates back to the 1960s when IBM developed virtual machines to allow multiple users to work on mainframe computers simultaneously.
The technology evolved steadily but gained widespread traction in the early 2000s with the growth of cloud computing and the rise of x86 server virtualisation. VMware, founded in 1998, played a key role in popularising the idea of running multiple virtual servers on a single physical box.
By the mid-2010s, virtualisation had become the norm in enterprise environments, and tools like Proxmox, KVM, Hyper-V, and VMware vSphere enabled more efficient data centre operations, disaster recovery, and workload management.
Advantages of Virtualisation
Virtualisation brings several practical benefits to IT environments:
1. Resource Optimisation
Running multiple VMs on a single server allows businesses to get the most out of their hardware investment. Instead of underutilised machines sitting idle, CPU, RAM, and storage can be dynamically shared across virtual workloads.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
New virtual servers can be provisioned in minutes. This is especially useful for development, testing, or launching new services without needing to buy and configure additional hardware.
3. Isolation and Security
Each VM operates independently. If one machine crashes or becomes compromised, it doesn’t necessarily affect the others. This isolation makes virtual environments more secure and manageable.
4. Disaster Recovery and Backup
Virtual machines are essentially files. They can be snapshotted, backed up, replicated, and restored much faster than traditional physical servers. In the event of hardware failure, systems can be brought back online rapidly.
5. Reduced Hardware Costs
Fewer physical servers mean reduced costs for power, cooling, rack space, and hardware maintenance — especially important for SMEs.
Virtualisation at FYDUS
At FYDUS, virtualisation underpins much of our internal infrastructure and services we offer to clients. We primarily use Proxmox VE, a powerful open-source hypervisor that supports both KVM for full virtualisation and LXC for lightweight containers.
This enables us to:
- Run multiple client web servers on isolated virtual machines
- Host internal systems (e.g., monitoring, backups, ticketing)
- Provide local and cloud-based infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS)
- Replicate environments for testing and development purposes
Whether you need to consolidate your servers, test new configurations, or move toward a hybrid cloud model, we can help plan and implement the right virtualised solution for your business.
The Future of Virtualisation
While containerisation (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes) is increasingly popular for application deployment, traditional virtualisation still plays a vital role — particularly for running legacy applications, isolating systems, and supporting infrastructure where full OS environments are required.
Technologies like virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), virtual firewalls, and virtual network appliances are expanding the role of virtualisation across business IT landscapes.
As businesses demand more agile, scalable, and cost-effective solutions, virtualisation will remain a key building block — whether on-premises, in the cloud, or in hybrid environments.
Conclusion
Virtualisation has revolutionised the way IT services are delivered and consumed. From resource efficiency and disaster recovery to flexibility and cost savings, it provides a robust foundation for businesses of all sizes.
At FYDUS IT Solutions, we specialise in designing, deploying, and maintaining virtualised environments tailored to your exact needs — whether you’re a small business moving off physical hardware or a growing company needing scalable infrastructure.
If you’re considering server upgrades, cloud migration, or virtual hosting, we’re here to help